From rugged deserts to lush forests, BLM land provides a diverse range of landscapes that attract hikers, campers, hunters, and nature lovers alike. But beyond recreation, these lands play a critical role in preserving biodiversity, supporting sustainable resource use, and fostering cultural connections. The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) oversees these vast tracts of land with a dual mission: to sustain the health and productivity of the land while also making it accessible for public enjoyment. This balance is no small feat, as BLM land often sits at the intersection of conservation, economic interests, and cultural preservation. With over 245 million acres under its management, the BLM ensures that these lands remain available for future generations to explore and cherish. Whether you're planning your next outdoor adventure or simply curious about the role of public lands in the U.S., understanding what BLM land is can deepen your appreciation for these invaluable resources. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of BLM land, answering common questions like "What is BLM land?" and exploring its uses, challenges, and significance. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of why these lands matter and how you can responsibly enjoy and protect them. So, let’s embark on this journey to uncover the wonders of BLM land and its role in shaping the American landscape.
Table of Contents
- What is BLM Land and Why Does It Matter?
- How Are BLM Lands Managed and Protected?
- What Activities Are Allowed on BLM Land?
- Why Are BLM Lands Important for Conservation?
- What Are the Challenges Facing BLM Lands Today?
- How Can You Responsibly Enjoy BLM Land?
- What Role Do Local Communities Play in BLM Land Management?
- Frequently Asked Questions About BLM Land
What is BLM Land and Why Does It Matter?
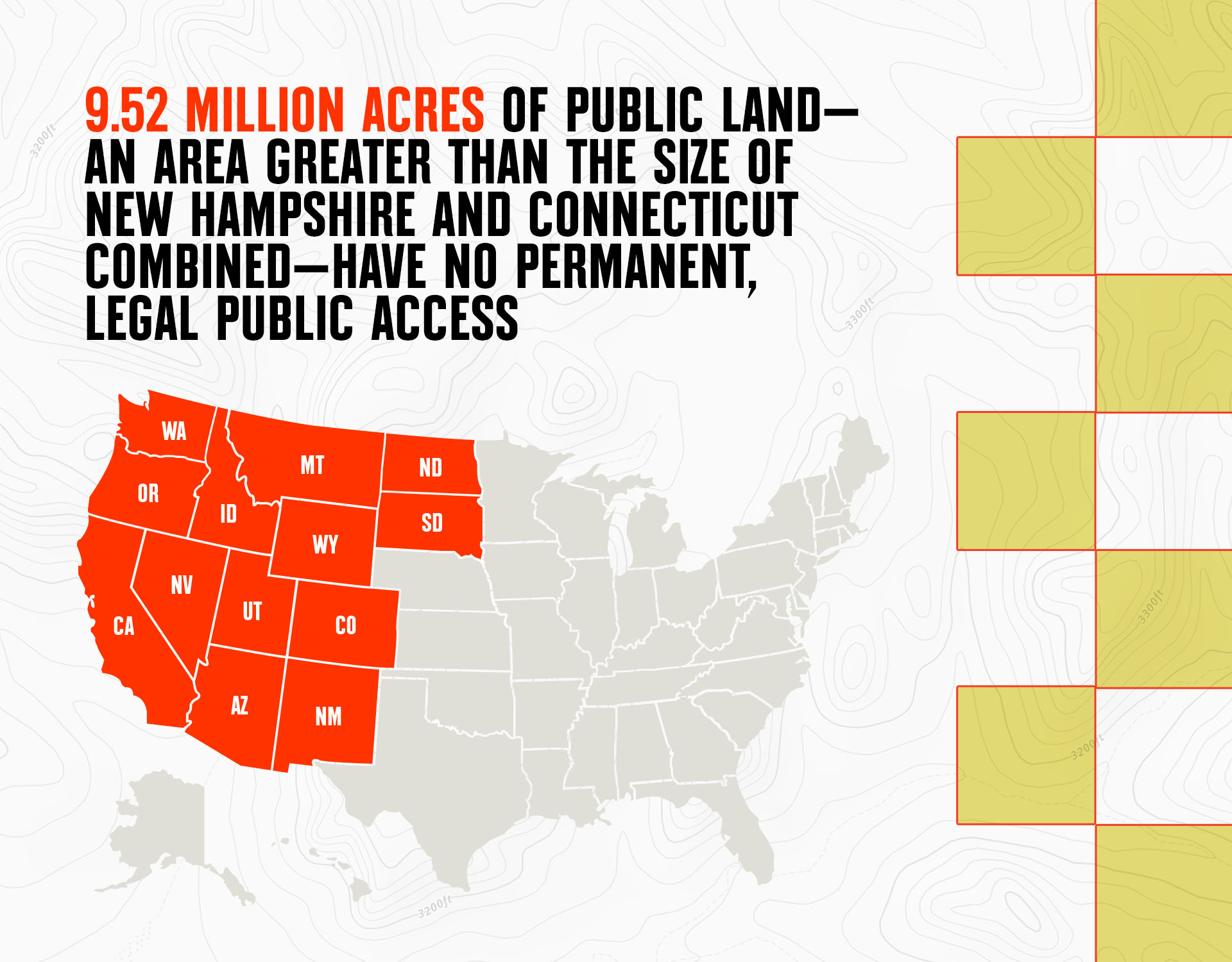
BLM land refers to the vast tracts of public land managed by the Bureau of Land Management, a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior. These lands are found primarily in the western United States, including states like Nevada, Utah, California, and Alaska. Spanning over 245 million acres, BLM land accounts for approximately one-tenth of the country’s total land area. This makes it a critical component of the nation’s natural and cultural heritage.
So, why does BLM land matter? First and foremost, these lands are a treasure trove of biodiversity, housing a wide variety of ecosystems and wildlife species. From the sagebrush steppe of the Great Basin to the towering red rock formations of Utah, BLM land supports habitats that are essential for both native flora and fauna. Additionally, these areas serve as vital corridors for migratory animals, ensuring the continuity of ecological processes.
Read also:Is Brad Mondo Dating Sophia Everything You Need To Know About Their Relationship
But the significance of BLM land extends beyond its ecological value. These lands are also deeply intertwined with the cultural and historical fabric of the United States. Many BLM-managed areas contain archaeological sites, ancient petroglyphs, and remnants of early human settlements. This rich cultural heritage offers a window into the lives of Indigenous peoples and early settlers, making BLM land a living museum of sorts. Whether you’re exploring its natural wonders or uncovering its historical secrets, BLM land invites you to connect with the past while appreciating the present.
How Are BLM Lands Managed and Protected?
The management of BLM lands is guided by a framework that seeks to balance multiple uses, including conservation, recreation, and resource extraction. This multifaceted approach ensures that these lands remain productive and accessible while also being protected for future generations. The BLM employs a variety of strategies to achieve this delicate balance, ranging from land-use planning to partnerships with local stakeholders.
Land-Use Planning: A Collaborative Process
One of the key tools in managing BLM land is the development of Resource Management Plans (RMPs). These plans outline how specific areas will be used and protected, taking into account factors such as ecological health, cultural significance, and public input. What makes these plans unique is their collaborative nature, as they involve input from local communities, tribes, scientists, and other stakeholders. This ensures that decisions about BLM land reflect a broad range of perspectives and priorities.
Monitoring and Enforcement: Keeping BLM Lands Healthy
To protect BLM lands, the agency conducts regular monitoring to assess the health of ecosystems and the impact of human activities. This includes tracking wildlife populations, monitoring water quality, and evaluating the effects of activities like grazing and mining. When violations occur—such as illegal dumping or unauthorized off-road vehicle use—the BLM enforces regulations to mitigate harm and hold offenders accountable.
Partnerships and Conservation Efforts
Another critical aspect of BLM land management is its partnerships with conservation organizations, tribal nations, and local governments. These collaborations often focus on large-scale conservation projects, such as habitat restoration, invasive species control, and wildfire prevention. For example, the BLM works closely with the National Wild Horse and Burro Program to manage wild horse populations in a way that balances ecological health with animal welfare.
What Activities Are Allowed on BLM Land?
One of the most appealing aspects of BLM land is the wide range of activities it supports. Whether you’re an outdoor enthusiast, a wildlife photographer, or someone looking to disconnect from the hustle and bustle of daily life, BLM land offers something for everyone. But what exactly can you do on these public lands?
Read also:Unveiling The Truth Patrick Swayzes Son Jason Whittle Dna Results Explained
Recreational Opportunities
Recreation is one of the primary uses of BLM land, attracting millions of visitors each year. Popular activities include:
- Hiking and Backpacking: With thousands of miles of trails, BLM land is a paradise for hikers and backpackers. From easy day hikes to multi-day treks, there’s no shortage of routes to explore.
- Camping: Many BLM areas offer dispersed camping, allowing visitors to pitch tents in remote locations. Some sites also have developed campgrounds with amenities like restrooms and picnic tables.
- Off-Roading and ATV Use: Designated areas permit off-road vehicle use, providing thrilling adventures for enthusiasts. However, it’s important to stick to approved routes to minimize environmental impact.
Wildlife and Nature Photography
For those who prefer a quieter experience, BLM land is a haven for wildlife and nature photography. The diverse landscapes and abundant wildlife offer endless opportunities to capture stunning images. Whether you’re photographing a golden eagle in flight or a field of wildflowers in bloom, BLM land provides a backdrop that’s hard to beat.
Resource Use and Extraction
In addition to recreation, BLM land supports responsible resource use, including grazing, mining, and energy development. These activities are carefully regulated to ensure they don’t compromise the land’s ecological integrity. For instance, grazing permits are issued with specific guidelines to prevent overgrazing, while mining operations must adhere to strict environmental standards.
Why Are BLM Lands Important for Conservation?
BLM lands play a pivotal role in conservation efforts across the United States. These vast tracts of land serve as refuges for countless species, protect critical habitats, and contribute to global biodiversity. But what makes BLM land so crucial for conservation?
Preserving Biodiversity
One of the primary reasons BLM lands are vital for conservation is their role in preserving biodiversity. These areas are home to a wide array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. For example, the sagebrush ecosystems of the western U.S. support species like the greater sage-grouse, which depends on these habitats for survival. By protecting BLM land, we ensure that these species have the space and resources they need to thrive.
Combating Climate Change
BLM lands also contribute to climate change mitigation by acting as carbon sinks. Forests, grasslands, and wetlands on these lands absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to offset greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, conservation efforts on BLM land often focus on restoring degraded areas, which can enhance their ability to sequester carbon.
Protecting Cultural and Historical Resources
Beyond their ecological importance, BLM lands are rich in cultural and historical resources. These areas contain archaeological sites, sacred landscapes, and artifacts that tell the story of America’s past. By preserving these resources, BLM land helps maintain the cultural heritage of Indigenous peoples and early settlers, ensuring that their stories are not lost to time.
What Are the Challenges Facing BLM Lands Today?
Despite their importance, BLM lands face a host of challenges that threaten their long-term sustainability. These challenges range from environmental pressures to competing land-use demands. Understanding these issues is crucial for finding solutions that protect these invaluable resources.
Environmental Threats
One of the most pressing challenges is environmental degradation, which can result from climate change, invasive species, and human activities. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns are altering ecosystems, making it harder for native species to survive. Invasive species, such as cheatgrass, further exacerbate these problems by outcompeting native plants and increasing wildfire risks.
Balancing Multiple Uses
Another challenge is balancing the multiple uses of BLM land. While recreation, conservation, and resource extraction are all important, they often come into conflict. For example, energy development projects can disrupt wildlife habitats, while increased recreational use can lead to soil erosion and habitat destruction. Finding a way to harmonize these competing interests is a constant challenge for land managers.
Funding and Resource Constraints
Finally, BLM lands are often hampered by limited funding and resources. Managing millions of acres requires significant financial and human resources, yet the BLM frequently operates with tight budgets. This can hinder efforts to monitor land health, enforce regulations, and implement conservation projects. Addressing these constraints is essential for ensuring the long-term viability of BLM land.
How Can You Responsibly Enjoy BLM Land?
As stewards of public lands, it’s our responsibility to enjoy BLM land in a way that minimizes our impact and preserves its beauty for future generations. But how can you ensure that your visit is both enjoyable and sustainable?
Leave No Trace Principles
One of the best ways to responsibly enjoy BLM land is by following the Leave No Trace principles. These guidelines emphasize minimizing your impact on the environment and include practices like packing out trash, staying on designated trails, and avoiding disturbing wildlife. By adhering to these principles, you can help keep BLM land pristine and enjoyable for everyone.
Respect Local Regulations
It’s also important to familiarize yourself with local regulations before visiting BLM land. These rules are designed to protect both the land and its visitors, so adhering to them is crucial. For example, some areas may have restrictions on campfires or require permits for certain activities. By respecting these regulations, you contribute to the sustainable use of BLM land.
Support Conservation Efforts
Finally, consider supporting conservation efforts on BLM land. This can include volunteering with local organizations, donating to conservation initiatives, or simply spreading awareness about the importance of these lands. Every little bit helps in ensuring that BLM land remains a national treasure for years to come.
What Role Do Local Communities Play in BLM Land Management?
Local communities are integral to the management and stewardship of BLM land. Their involvement ensures that land-use decisions reflect the needs and values of the people who live nearby, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility. But what exactly is the role of local communities in managing these public lands?