Stop limit orders are a powerful tool in the world of trading, allowing investors to manage risk and maximize profits with precision. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting, understanding how to use stop limit orders can make a significant difference in your trading strategy. This type of order combines the features of a stop order and a limit order, providing traders with greater control over their buy and sell transactions. By setting a stop price and a limit price, traders can protect themselves from unexpected market volatility while ensuring their orders are executed at a price they’re comfortable with.
In today’s fast-paced financial markets, where prices can fluctuate in the blink of an eye, having a stop limit order in your toolkit is essential. It acts as a safeguard, ensuring that your trades are executed only when certain conditions are met. This dual-layered approach not only helps in minimizing losses but also allows traders to lock in profits during favorable market movements. For example, if you’re holding a stock that’s gaining value, a stop limit order can help you sell it when it reaches a specific price, ensuring you don’t miss out on potential gains.
As we dive deeper into the mechanics of stop limit orders, you’ll discover how they differ from other types of orders, such as market orders and stop-loss orders. We’ll explore real-world scenarios where stop limit orders can be particularly beneficial and provide actionable tips to help you implement them effectively in your trading strategy. Whether you’re trading stocks, cryptocurrencies, or commodities, mastering stop limit orders can give you the edge you need to succeed in the market.
Read also:Who Is Julianna Farrait Young Discover Her Inspiring Journey
Table of Contents
- What is a Stop Limit Order?
- How Does a Stop Limit Order Work?
- Why Use a Stop Limit Order in Your Trading?
- How Can Stop Limit Orders Help Manage Risk?
- What Are the Differences Between Stop Limit and Stop-Loss Orders?
- Are There Any Downsides to Using Stop Limit Orders?
- How to Set Up a Stop Limit Order on Your Trading Platform?
- What Are Some Tips for Using Stop Limit Orders Effectively?
What is a Stop Limit Order?
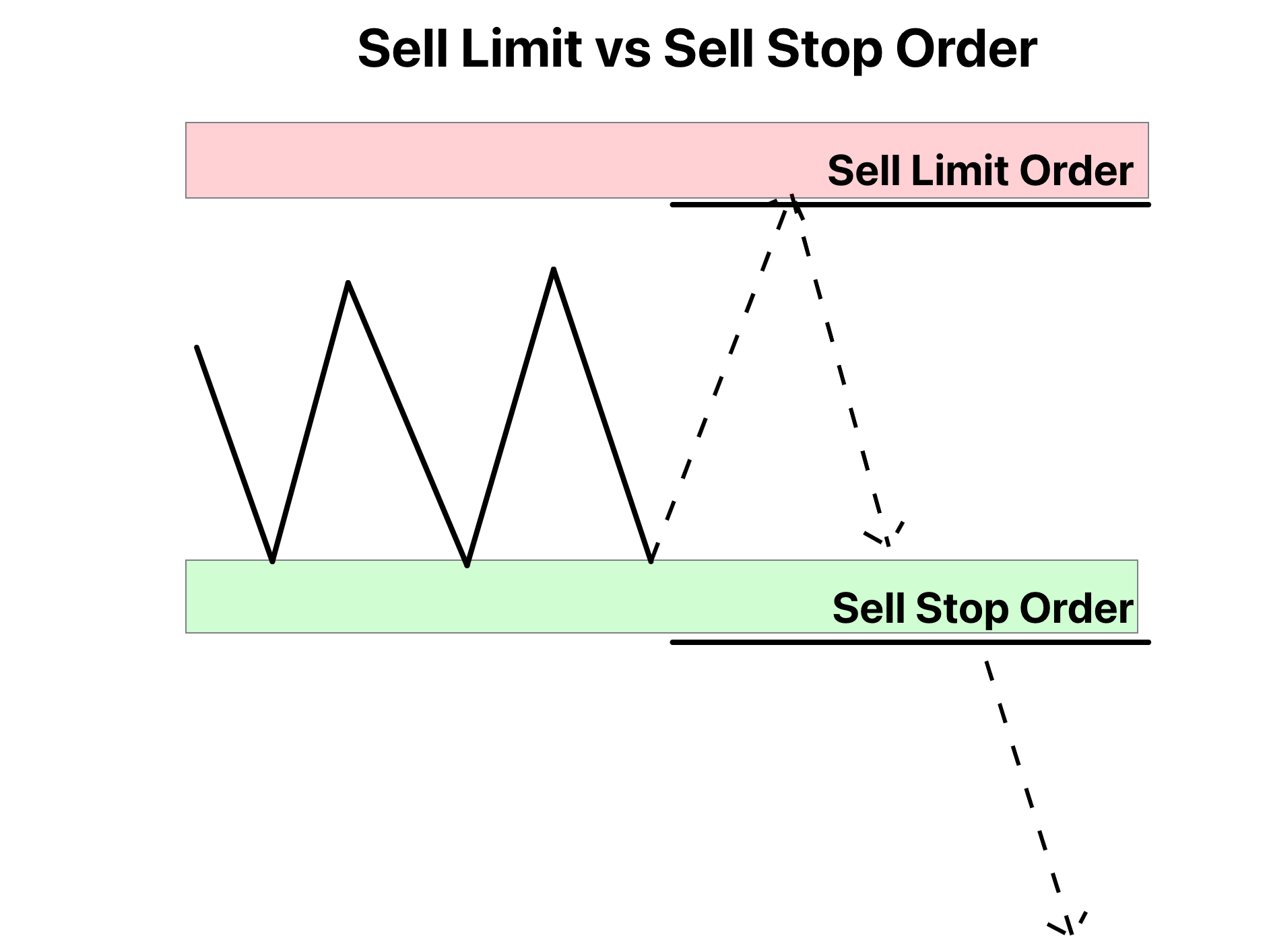
A stop limit order is a type of trade order that combines the features of a stop order and a limit order. Essentially, it allows traders to set two prices: a stop price and a limit price. The stop price acts as a trigger, initiating the order when the market reaches that level. Once the stop price is hit, the order becomes a limit order, meaning the trade will only execute at the specified limit price or better. This dual mechanism provides traders with greater control over their trades, ensuring they don’t sell or buy at prices that are unfavorable to them.
For instance, imagine you own shares of a stock currently trading at $50, but you’re concerned about a potential drop in price. You could set a stop limit order with a stop price of $48 and a limit price of $47. If the stock price falls to $48, the order is triggered, but it will only execute if the price stays above $47. This ensures you don’t sell your shares at a price lower than $47, even if the market experiences sudden volatility.
Stop limit orders are particularly useful in volatile markets where prices can swing dramatically in a short period. By combining the protective features of a stop order with the precision of a limit order, traders can better manage their risk while maintaining flexibility in their trading strategies. However, it’s important to note that stop limit orders are not guaranteed to execute, especially in fast-moving markets where prices might skip over the limit price entirely.
How Does a Stop Limit Order Work?
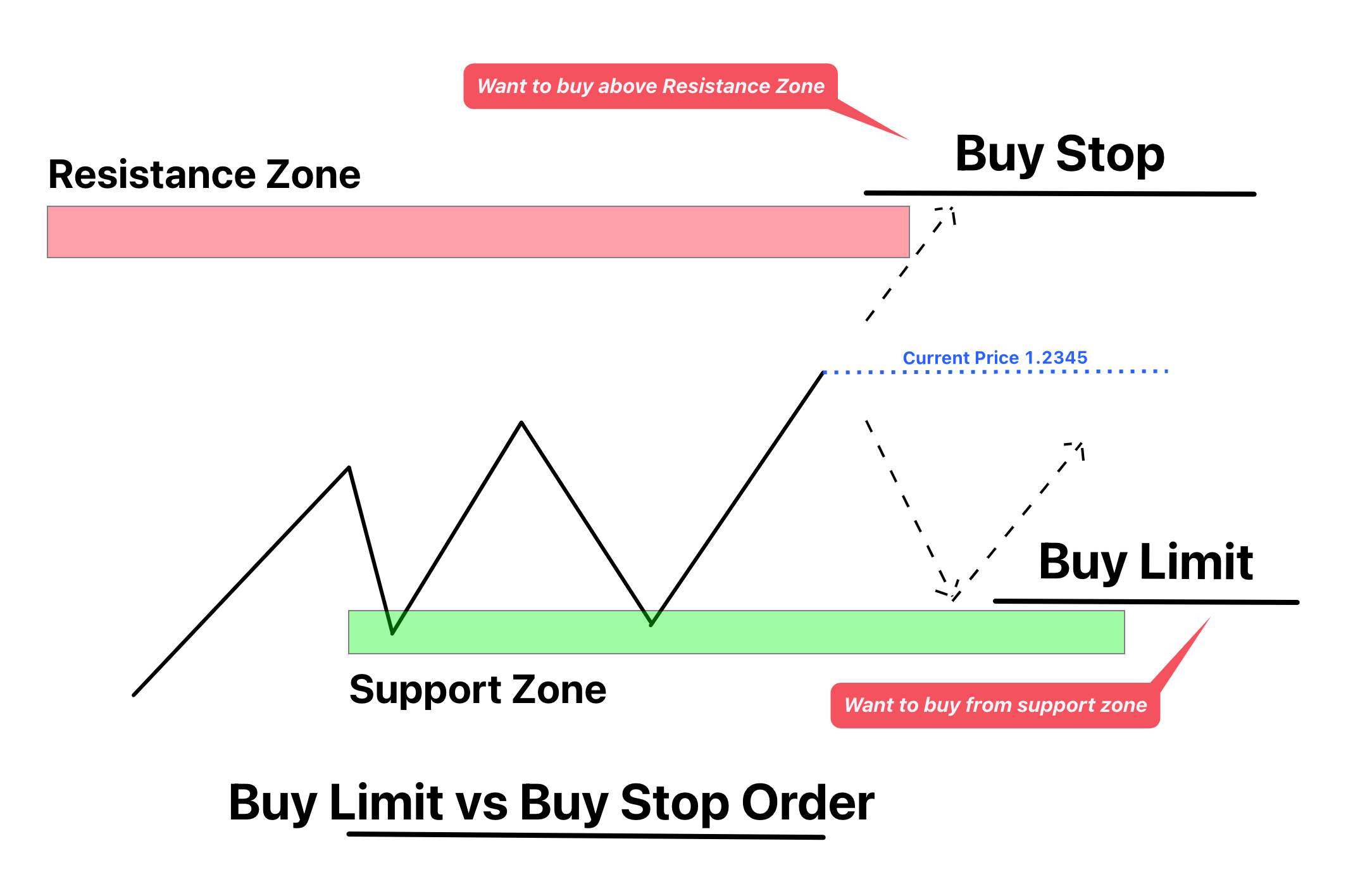
To understand how a stop limit order works, let’s break it down step by step. First, the trader sets a stop price, which acts as the trigger point for the order. Once the market price reaches or surpasses this stop price, the order transitions into a limit order. At this stage, the limit price comes into play, dictating the highest price the trader is willing to pay (for a buy order) or the lowest price they’re willing to accept (for a sell order).
Here’s a practical example to illustrate this process. Suppose you’re interested in purchasing shares of a stock currently trading at $100. You set a stop limit order with a stop price of $105 and a limit price of $107. If the stock price rises to $105, the stop price is triggered, and your order becomes a limit order. The trade will only execute if the price stays below $107. This ensures you don’t end up paying more than $107 per share, even if the market experiences a sudden spike in price.
While stop limit orders provide traders with greater control, they also come with certain limitations. One key consideration is that the order may not execute if the market moves too quickly, bypassing the limit price. For example, if the stock price jumps from $105 to $110 in a matter of seconds, your limit order at $107 may remain unfilled. This is why traders need to carefully assess market conditions and set realistic stop and limit prices to increase the likelihood of execution.
Read also:Understanding Fox News Salaries A Comprehensive Guide
Why Use a Stop Limit Order in Your Trading?
Using a stop limit order in your trading strategy offers several advantages, particularly in volatile markets. One of the primary benefits is the ability to protect your investments from significant losses. By setting a stop price, you can ensure that your order is triggered only when the market reaches a specific level, allowing you to exit a position before it incurs substantial losses. This is especially valuable in fast-moving markets where prices can change rapidly.
What Are the Key Benefits of Stop Limit Orders?
Stop limit orders provide traders with a unique blend of control and flexibility. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Risk Management: By setting a stop price and a limit price, traders can define their risk tolerance and avoid executing trades at unfavorable prices.
- Price Protection: Unlike market orders, which execute at the current market price, stop limit orders ensure that trades are executed only within a specified price range.
- Flexibility: Traders can use stop limit orders for both buying and selling, making them versatile tools for various trading strategies.
How Do Stop Limit Orders Enhance Trading Strategies?
Stop limit orders can be integrated into a variety of trading strategies, from day trading to long-term investing. For day traders, stop limit orders help lock in profits by automatically selling shares when they reach a target price. For long-term investors, they act as a safeguard against sudden market downturns, ensuring that positions are exited before losses become unsustainable. Additionally, stop limit orders can be used to enter positions at favorable prices, such as buying a stock when it dips to a specific level.
How Can Stop Limit Orders Help Manage Risk?
Risk management is a cornerstone of successful trading, and stop limit orders play a crucial role in this process. By allowing traders to set predefined exit points, stop limit orders help mitigate the impact of market volatility. For example, if you’re holding a stock that’s experiencing a downturn, a stop limit order can ensure you sell your shares before the price drops too low. This proactive approach to risk management can save traders from significant financial losses.
Moreover, stop limit orders can be tailored to suit different risk appetites. Conservative traders might set their stop and limit prices close together to minimize risk, while more aggressive traders may allow for a wider range to increase the likelihood of execution. This flexibility makes stop limit orders a valuable tool for traders of all experience levels.
However, it’s important to recognize that stop limit orders are not foolproof. In highly volatile markets, there’s always a risk that the order may not execute if the price moves too quickly. To address this, traders should regularly monitor their positions and adjust their stop and limit prices as needed to align with changing market conditions.
What Are the Differences Between Stop Limit and Stop-Loss Orders?
While both stop limit orders and stop-loss orders are designed to manage risk, they operate in fundamentally different ways. A stop-loss order becomes a market order once the stop price is reached, meaning it will execute at the best available price. This can lead to slippage, where the trade is executed at a price worse than expected, particularly in volatile markets.
In contrast, a stop limit order becomes a limit order when the stop price is triggered, ensuring that the trade is executed only at the specified limit price or better. This provides traders with greater control over the execution price but comes with the risk of the order not being filled if the market moves too quickly. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right type of order based on your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Which Order Type is Right for You?
The choice between a stop limit order and a stop-loss order depends on your trading strategy and risk management preferences. If you prioritize execution certainty, a stop-loss order may be more suitable. However, if you’re willing to accept the risk of non-execution in exchange for price control, a stop limit order is the better option.
Are There Any Downsides to Using Stop Limit Orders?
While stop limit orders offer numerous benefits, they also come with certain drawbacks. One of the main disadvantages is the possibility of the order not being executed. If the market moves too quickly, bypassing the limit price, the order may remain unfilled. This can be particularly problematic in highly volatile markets where price swings are common.
What Are the Risks of Non-Execution?
Non-execution is a significant risk associated with stop limit orders. For example, if you set a stop limit order to sell a stock at a stop price of $50 and a limit price of $49, but the price drops from $50 to $48 in a matter of seconds, your order may not execute. This can leave you exposed to further losses if the market continues to decline.
How Can Traders Mitigate These Risks?
To mitigate the risks of non-execution, traders can take several steps. First, they can set wider limits between the stop price and the limit price to increase the likelihood of execution. Second, they can monitor their positions closely and adjust their orders as market conditions change. Finally, they can use stop limit orders in conjunction with other risk management tools, such as diversification and position sizing, to create a more robust trading strategy.
How to Set Up a Stop Limit Order on Your Trading Platform?
Setting up a stop limit order on your trading platform is a straightforward process, but the exact steps may vary depending on the platform you’re using. Generally, you’ll need to navigate to the order entry section, select “Stop Limit” as the order type, and input your desired stop price and limit price. It’s important to double-check your inputs to ensure accuracy before submitting the order.
Most trading platforms provide tutorials or guides to help users understand how to set up different types of orders. If you’re new to stop limit orders, it’s a good idea to practice with a demo account before using them in live trading. This allows you to familiarize yourself with the process and gain confidence in your ability to execute trades effectively.
What Are Some Tips for Using Stop Limit Orders Effectively?
To maximize the effectiveness of stop limit orders, consider the following tips:
- Set Realistic Prices: Ensure your stop and limit prices are based on realistic market conditions to increase the likelihood of execution.
- Monitor the Market: Keep an eye on market trends and adjust your orders as needed to reflect changing conditions.
- Combine with Other Tools: Use stop limit orders alongside other risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, for a comprehensive approach.
What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid?
One common mistake is setting the limit price too close to the stop price, which can result in non-execution. Another is failing to adjust orders in response to market volatility. By avoiding these pitfalls, traders can use stop limit orders more effectively to achieve their