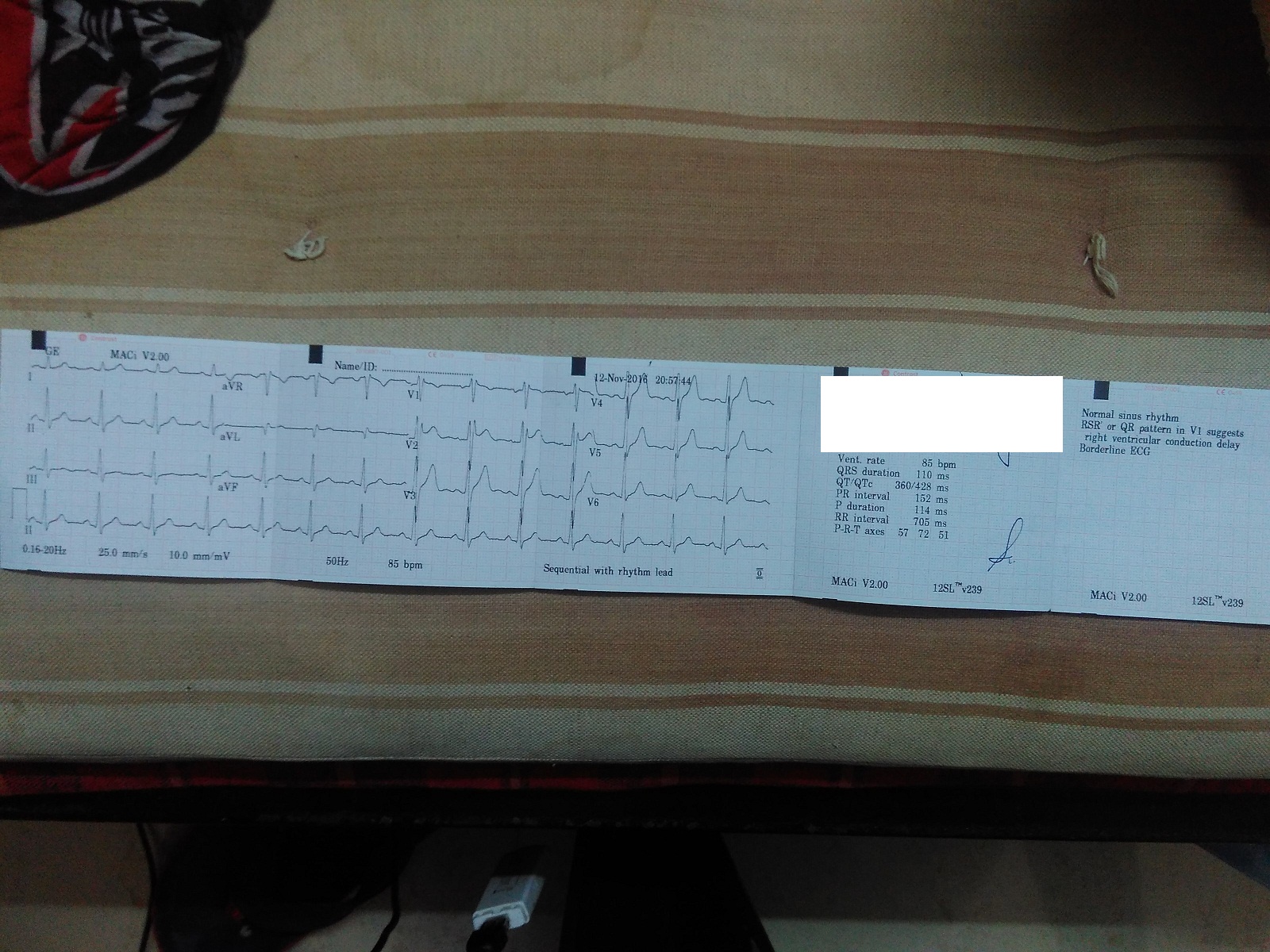
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart. When a doctor refers to a "borderline ECG," it often indicates that the results are not entirely normal but also not definitively abnormal. This term can raise questions and concerns, especially for individuals who are unfamiliar with medical terminology. A borderline ECG meaning typically suggests that while there may be slight irregularities in the heart's rhythm or structure, these findings are not severe enough to warrant an immediate diagnosis of heart disease. However, it does signal the need for further evaluation to rule out underlying conditions. To better understand the significance of a borderline ECG, it's essential to know how an ECG works and what it measures. An ECG records the timing and strength of electrical signals in the heart, providing insights into heart rate, rhythm, and potential structural abnormalities. A borderline result may arise from various factors, such as stress, electrolyte imbalances, or even minor heart conditions that don't yet require intervention. While the term "borderline" might sound alarming, it often serves as a precautionary flag rather than a definitive diagnosis. Doctors typically recommend additional tests, such as a stress test or echocardiogram, to gather more information and ensure the heart is functioning optimally. This article will delve deeper into the meaning of a borderline ECG, exploring its potential causes, implications, and what steps you should take if you receive this result. We'll also address common questions, such as "What does a borderline ECG mean for my health?" and "How can I improve my heart health after a borderline ECG?" By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of this medical term and feel empowered to discuss it confidently with your healthcare provider.
- What Does Borderline ECG Mean?
- How Is a Borderline ECG Diagnosed?
- What Are the Common Causes of a Borderline ECG?
- Is a Borderline ECG a Sign of Heart Disease?
- How Can You Improve Your Heart Health After a Borderline ECG?
- What Tests Follow a Borderline ECG?
- What Should You Discuss With Your Doctor?
- Frequently Asked Questions About Borderline ECG
What Does Borderline ECG Mean?
A borderline ECG refers to an electrocardiogram result that falls between normal and abnormal readings. While it may not indicate a serious heart condition, it does suggest that certain aspects of your heart's electrical activity are slightly irregular. These irregularities could be related to heart rate, rhythm, or even the heart's physical structure. For example, a borderline ECG might show a slightly elevated heart rate, minor changes in the ST segment, or subtle variations in the QRS complex. These findings are not definitive proof of heart disease but do warrant further investigation to ensure there are no underlying issues.
It's important to note that a borderline ECG meaning can vary depending on the context. In some cases, the irregularities may be temporary and caused by external factors such as stress, caffeine intake, or dehydration. In other instances, a borderline result could be an early indicator of a more serious condition, such as arrhythmia or cardiomyopathy. This is why doctors often recommend additional tests to confirm or rule out any potential problems. Understanding the nuances of a borderline ECG can help you approach the situation with clarity and confidence, ensuring you take the necessary steps to protect your heart health.
Read also:Renowned Actress Kathleen Quinlan A Closer Look At Her Life And Career
How Is a Borderline ECG Diagnosed?
The process of diagnosing a borderline ECG begins with the actual electrocardiogram test. During this non-invasive procedure, electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs to record the heart's electrical activity. The ECG machine then generates a graph that represents the timing and strength of these electrical signals. A cardiologist or trained healthcare professional will analyze the graph to determine whether the results fall within normal parameters. If the findings are slightly outside the normal range but not severe enough to indicate a clear abnormality, the ECG is classified as "borderline."
What Factors Influence the Diagnosis?
Several factors can influence whether an ECG is labeled as borderline. These include:
- Heart Rate: A heart rate that is slightly above or below the normal range (60-100 beats per minute) can contribute to a borderline classification.
- Rhythm Irregularities: Minor variations in heart rhythm, such as occasional skipped beats, may lead to a borderline result.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Low levels of potassium or magnesium can affect the heart's electrical activity, resulting in a borderline ECG.
- External Influences: Stress, caffeine, or even a recent workout can temporarily alter ECG readings.
Why Is Further Testing Important?
While a borderline ECG may not indicate an immediate health risk, it is crucial to follow up with additional tests to ensure there are no underlying conditions. These tests may include a Holter monitor, stress test, or echocardiogram, each of which provides more detailed insights into the heart's function. By combining the results of these tests with the initial ECG, healthcare providers can make a more accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment or lifestyle changes.
What Are the Common Causes of a Borderline ECG?
A borderline ECG can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from benign and temporary factors to more serious underlying conditions. One of the most common causes is stress or anxiety, which can temporarily elevate the heart rate and alter the heart's electrical activity. Similarly, consuming excessive caffeine or alcohol before the test can lead to irregularities in the ECG readings. Dehydration is another frequent culprit, as it can disrupt the balance of electrolytes in the body, affecting the heart's ability to function optimally.
Could a Borderline ECG Be Linked to Heart Conditions?
In some cases, a borderline ECG may be an early warning sign of a heart condition. For instance, minor changes in the ST segment or T wave can indicate ischemia, a condition where the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Other potential causes include arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, which can cause irregular heartbeats. Structural abnormalities, like an enlarged heart or thickened heart walls, may also contribute to a borderline ECG. While these conditions are not always immediately life-threatening, they do require careful monitoring and management to prevent complications.
How Do Lifestyle Factors Play a Role?
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact the likelihood of receiving a borderline ECG. Smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity are all risk factors for heart disease and can contribute to abnormal ECG readings. Additionally, certain medications, such as beta-blockers or antiarrhythmic drugs, can alter the heart's electrical activity and lead to a borderline result. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to improve their heart function.
Read also:Ultimate Guide To Green Valley Ranch Everything You Need To Know
Is a Borderline ECG a Sign of Heart Disease?
Receiving a borderline ECG can naturally lead to concerns about heart disease. However, it's important to remember that a borderline result does not automatically mean you have a serious heart condition. In many cases, the irregularities detected on the ECG are minor and may not pose any immediate health risks. For example, slight variations in heart rate or rhythm can occur in healthy individuals due to factors like stress or physical activity. These changes are often temporary and resolve on their own without medical intervention.
When Should You Be Concerned About Heart Disease?
While a borderline ECG is not a definitive indicator of heart disease, it does serve as a warning sign that should not be ignored. If you have additional risk factors, such as a family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes, the likelihood of an underlying condition increases. Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fatigue should also prompt further investigation, as they may indicate a more serious issue. In such cases, your doctor may recommend additional diagnostic tests, such as a coronary angiogram or cardiac MRI, to assess the health of your heart in greater detail.
What Steps Can You Take to Rule Out Heart Disease?
If you're concerned about the possibility of heart disease, there are several proactive steps you can take. First, schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your ECG results and any symptoms you may be experiencing. They may recommend lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking, to reduce your risk of developing heart disease. Additionally, managing conditions like high cholesterol or hypertension can significantly improve your heart health and lower the likelihood of complications. By staying informed and taking action, you can address potential risks and ensure your heart remains in good condition.
How Can You Improve Your Heart Health After a Borderline ECG?
After receiving a borderline ECG, taking steps to improve your heart health is essential. One of the most effective ways to do this is by adopting a heart-healthy diet. Focus on consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, which can help reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular function. Incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your meals can also provide the nutrients your heart needs to function optimally. Avoiding processed foods, excessive salt, and sugary beverages is equally important, as these can contribute to high blood pressure and other risk factors for heart disease.
Why Is Exercise Important for Heart Health?
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of maintaining a healthy heart. Engaging in moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week can strengthen your heart muscle, improve circulation, and lower your risk of heart disease. Exercise also helps manage weight, reduce stress, and improve cholesterol levels, all of which contribute to better heart health. If you're new to exercise or have concerns about your fitness level, consult with your doctor to develop a safe and effective workout plan tailored to your needs.
What Lifestyle Changes Should You Consider?
Beyond diet and exercise, making other lifestyle changes can significantly impact your heart health. Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps you can take, as smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Reducing alcohol consumption and managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can also benefit your heart. Additionally, ensuring you get adequate sleep each night is crucial, as poor sleep has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. By addressing these areas, you can take control of your health and reduce the likelihood of future heart-related issues.
What Tests Follow a Borderline ECG?
After a borderline ECG, your doctor may recommend additional tests to gather more information about your heart's health. One common follow-up test is a Holter monitor, a portable device that records your heart's electrical activity over 24 to 48 hours. This extended monitoring can help identify irregularities that may not appear during a standard ECG. Another test that might be suggested is a stress test, where you exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike while your heart's activity is monitored. This test can reveal how your heart responds to physical exertion and whether any abnormalities become more pronounced under stress.
What Is the Role of an Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram is another valuable diagnostic tool that may follow a borderline ECG. This test uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart's structure and function. It can help identify issues such as valve problems, heart muscle damage, or an enlarged heart, which might not be evident on an ECG. An echocardiogram provides a comprehensive view of the heart's chambers, valves, and blood flow, allowing doctors to assess whether the borderline ECG findings are linked to structural abnormalities or other underlying conditions.
Why Are Blood Tests Important?
Blood tests are often part of the follow-up process after a borderline ECG. These tests can measure levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, and other markers that indicate your risk of heart disease. Additionally, blood tests can detect electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium or magnesium, which can affect heart function and contribute to abnormal ECG readings. By analyzing these results alongside your ECG