Have you ever wondered what "BLM land" actually means? If you're an outdoor enthusiast, a history buff, or simply curious about public lands, this term might have caught your attention. BLM land refers to areas managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior. These lands cover a vast expanse of the United States, offering opportunities for recreation, conservation, and resource management. Understanding the significance of BLM land meaning is essential for anyone interested in exploring these unique landscapes or learning about their role in American history and ecology.
BLM-managed lands are often described as "America's backyard," encompassing over 245 million acres of diverse terrains, from deserts and forests to mountains and grasslands. These areas are not only home to stunning natural beauty but also serve as vital habitats for wildlife, resources for scientific research, and spaces for outdoor recreation. Whether you're planning a camping trip, studying environmental policies, or simply curious about land management, knowing the ins and outs of BLM land meaning can deepen your appreciation for these public treasures.
In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of BLM land meaning, exploring its history, purpose, and the opportunities it provides for public use. From understanding how these lands are managed to uncovering their ecological and cultural significance, we aim to provide a comprehensive guide that is both informative and engaging. Whether you're a seasoned explorer or a newcomer to the concept of public lands, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make the most of your BLM land adventures.
Read also:Molly Baz Culinary Innovator Cookbook Author And Social Media Star
Table of Contents
- What Is BLM Land Meaning?
- How Are BLM Lands Managed?
- Why Are BLM Lands Important for Conservation?
- Can You Camp on BLM Land?
- What Activities Are Allowed on BLM Land?
- How Does BLM Land Support Local Communities?
- What Are the Challenges Facing BLM Lands?
- How Can You Get Involved with BLM Lands?
- FAQs About BLM Land Meaning
What Is BLM Land Meaning?
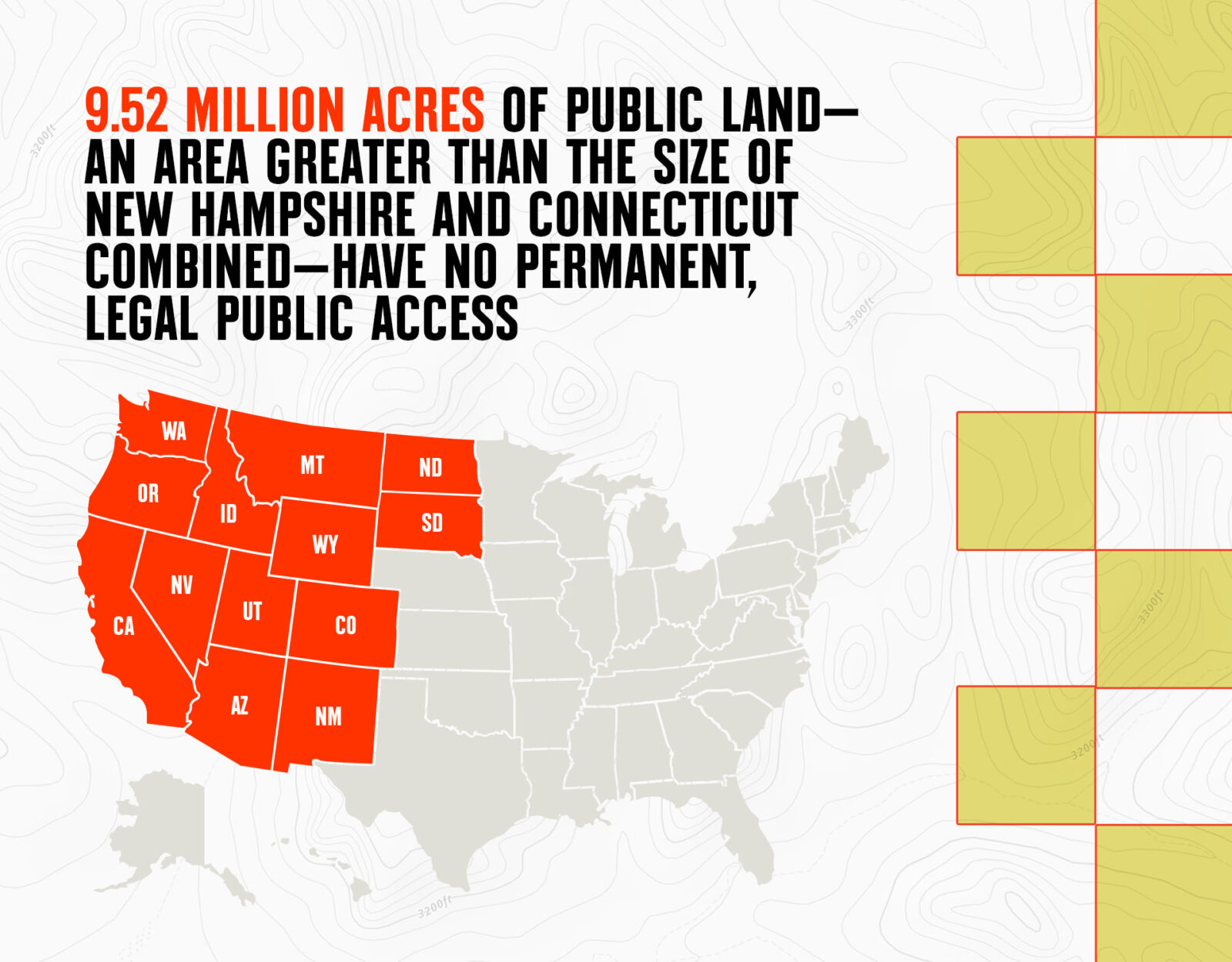
At its core, "BLM land meaning" refers to the lands managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), a federal agency established in 1946. These lands are part of the public domain, meaning they are owned by the U.S. government and managed for the benefit of all citizens. The BLM oversees approximately 245 million acres, primarily in the western United States, including states like Nevada, Alaska, Utah, and California. This vast expanse represents about 10% of the total land area in the country, making BLM one of the largest land managers in the nation.
BLM lands are characterized by their diversity. They include deserts, forests, grasslands, wetlands, and even coastal areas. These landscapes are not only visually stunning but also ecologically significant, providing habitats for countless species of plants and animals. For example, the sagebrush steppe ecosystems found on BLM lands are home to species like the greater sage-grouse, which depend on these habitats for survival. Additionally, BLM lands often hold cultural and historical significance, with ancient Native American sites, pioneer trails, and mining relics scattered throughout.
Understanding BLM land meaning also involves recognizing the agency's dual mandate: to balance conservation with resource use. This includes managing activities like grazing, mining, energy development, and recreation while ensuring the long-term health of the land. This delicate balance is one of the key challenges facing BLM land management today. By learning about the BLM's mission and the lands it oversees, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the role these public spaces play in our lives.
What Does "BLM" Stand For?
Many people confuse the acronym "BLM" with the Black Lives Matter movement, but in this context, it stands for the Bureau of Land Management. This federal agency was created to consolidate the management of public lands previously overseen by the General Land Office and the U.S. Grazing Service. Its primary mission is to sustain the health, diversity, and productivity of public lands for the use and enjoyment of present and future generations.
How Does BLM Land Differ from National Parks?
While both BLM lands and national parks are public spaces, they serve different purposes and are managed differently. National parks are primarily focused on preserving natural and cultural resources for public enjoyment, often with stricter regulations on activities like hunting and off-road vehicle use. BLM lands, on the other hand, allow for a wider range of uses, including grazing, mining, and energy development, alongside recreational activities. This flexibility reflects the BLM's mandate to balance multiple uses with conservation.
How Are BLM Lands Managed?
The management of BLM lands is guided by a combination of federal laws, policies, and public input. One of the key frameworks is the Federal Land Policy and Management Act (FLPMA) of 1976, which established the principles of multiple-use and sustained yield. These principles mean that BLM lands are managed to accommodate a variety of uses, from recreation and conservation to resource extraction, while ensuring that these activities do not degrade the land's long-term health.
Read also:Discovering Allysa Rose Unveiling The Life And Legacy Of An Inspiring Personality
BLM land managers work closely with local communities, stakeholders, and scientists to develop land-use plans, also known as Resource Management Plans (RMPs). These plans outline how specific areas will be managed, balancing competing interests and addressing environmental concerns. For example, an RMP might designate certain areas for conservation while allowing grazing or energy development in others. Public participation is a crucial part of this process, with opportunities for individuals and organizations to provide input during planning stages.
Another important aspect of BLM land management is the agency's role in wildfire prevention and response. BLM lands are often prone to wildfires, particularly in arid regions like the western United States. The agency collaborates with other federal, state, and local entities to implement fire management strategies, including controlled burns and vegetation management, to reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfires. These efforts not only protect ecosystems but also safeguard nearby communities.
What Are the Key Challenges in Managing BLM Lands?
Managing BLM lands is no easy task, as it involves balancing diverse interests and addressing complex environmental issues. One of the biggest challenges is reconciling the demands of resource extraction, such as mining and oil drilling, with conservation goals. These activities can sometimes conflict with efforts to protect wildlife habitats or preserve cultural sites. Additionally, climate change poses a growing threat to BLM lands, with rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns affecting ecosystems and water resources.
How Does Public Input Influence BLM Land Management?
Public input is a cornerstone of BLM land management, ensuring that decisions reflect the needs and values of diverse stakeholders. The agency holds public meetings, conducts environmental assessments, and solicits comments during the planning process. This collaborative approach helps build trust and ensures that management decisions are transparent and inclusive. For example, local communities might advocate for increased recreational opportunities, while conservation groups might push for stronger protections for endangered species.
Why Are BLM Lands Important for Conservation?
BLM lands play a critical role in conservation efforts across the United States. These areas provide essential habitats for a wide range of species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. For example, the sagebrush ecosystems of the western United States support over 350 species of plants and animals, including the iconic greater sage-grouse. By protecting these habitats, BLM lands contribute to the preservation of biodiversity and the resilience of ecosystems in the face of environmental challenges.
In addition to their ecological significance, BLM lands are also important for combating climate change. Many of these areas serve as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate the effects of global warming. For instance, forests and grasslands on BLM lands store large amounts of carbon, making them valuable assets in the fight against climate change. The agency is increasingly prioritizing climate resilience in its management practices, working to protect these natural resources for future generations.
BLM lands also offer opportunities for scientific research and education. Researchers study these areas to better understand ecological processes, species interactions, and the impacts of human activities on natural systems. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and informing policy decisions. Moreover, BLM lands provide outdoor classrooms where students and educators can learn about geology, biology, and environmental science firsthand.
What Are Some Success Stories in BLM Land Conservation?
Over the years, the BLM has achieved several notable successes in conservation. One example is the establishment of the National Conservation Lands, a network of protected areas that includes national monuments, wilderness areas, and wild and scenic rivers. These designations help safeguard some of the most ecologically and culturally significant landscapes on BLM lands. Another success story is the agency's work to restore degraded habitats, such as riparian areas and wetlands, which are vital for wildlife and water quality.
How Do BLM Lands Support Indigenous Communities?
BLM lands often overlap with traditional territories of Indigenous peoples, who have deep cultural and spiritual connections to these landscapes. The agency works with tribes to protect sacred sites, preserve cultural resources, and promote traditional land uses like hunting and gathering. This collaboration is an important step toward recognizing and honoring the contributions of Indigenous communities to land stewardship.
Can You Camp on BLM Land?
Yes, camping is one of the most popular activities on BLM lands, offering a chance to experience the great outdoors in a more remote and unspoiled setting. Unlike national parks, which often have designated campgrounds and amenities, BLM lands typically allow dispersed camping, meaning you can set up camp almost anywhere as long as you follow basic guidelines. This flexibility makes BLM lands a favorite destination for adventurers seeking solitude and a closer connection to nature.
When camping on BLM land, it's important to follow Leave No Trace principles, which emphasize minimizing your impact on the environment. This includes packing out all trash, avoiding damage to vegetation, and respecting wildlife. Additionally, campfires may be restricted in certain areas, especially during fire season, so it's a good idea to check local regulations before your trip. Many BLM lands also have designated recreation areas with amenities like restrooms and picnic tables, providing a more developed camping experience if you prefer.
Another advantage of camping on BLM land is the opportunity to explore diverse landscapes and activities. Whether you're hiking in the desert, fishing in a mountain stream, or stargazing under pristine night skies, BLM lands offer endless possibilities for adventure. Some areas even allow off-road vehicle use, making them ideal for ATV enthusiasts and other motorized recreationists.
What Are the Rules for Dispersed Camping on BLM Land?
Dispersed camping on BLM land comes with a few basic rules to ensure safety and environmental protection. First, you should camp at least 200 feet away from water sources to avoid contaminating them. Second, stay on durable surfaces like established campsites or gravel areas to minimize soil erosion. Finally, always check for any specific restrictions or permit requirements in the area you plan to visit, as these can vary depending on location and season.
Are There Any Fees for Camping on BLM Land?
In most cases, camping on BLM land is free, especially for dispersed camping. However, some developed recreation areas or campgrounds may charge a nominal fee to cover maintenance and amenities. Additionally, certain activities like off-road vehicle use or hunting may require permits or licenses. It's always a good idea to research the specific area you plan to visit and confirm any associated costs beforehand.
What Activities Are Allowed on BLM Land?
BLM lands are incredibly versatile, offering a wide range of recreational activities for people of all interests and skill levels. Whether you're an avid hiker, a fishing enthusiast, or a photography buff, you're likely to find something that suits your passion. One of the most popular activities is hiking, with thousands of miles of trails winding through diverse terrains. These trails range from easy nature walks to challenging backcountry routes, providing opportunities for both casual explorers and seasoned adventurers.
Fishing is another favorite pastime on BLM lands, thanks to the abundance of rivers, lakes, and streams teeming with fish. Many of these water bodies are home to native species like trout and bass, making them ideal destinations for anglers. Hunting is also permitted in designated areas, with regulations varying by state and season. Wildlife enthusiasts can spot a variety of animals, from elk and deer to birds of prey, adding to the allure of these landscapes.
For those who enjoy motorized recreation, BLM lands offer extensive opportunities for off